Mumbai is currently facing a concerning rise in vector-borne illnesses, with malaria cases seeing a sharp jump over the last fortnight. According to the Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC), the city has been reporting an average of 38 malaria and 28 dengue cases every day since mid-August.
Between January and September 15, 2025, Mumbai recorded 6,277 malaria cases, along with 2,724 dengue and 558 leptospirosis cases. Compared to last year, malaria cases have risen by nearly 38%, dengue by 17.8%, and leptospirosis by 18%.

Canva
About Malaria
As per the Cleveland Clinic, malaria is a potentially life-threatening disease caused by Plasmodium parasites, which spread to humans through bites from infected Anopheles mosquitoes. While most common in hot and humid tropical regions, cases are on the rise in South Asia, including India. Without timely treatment, malaria can lead to severe complications such as brain damage, organ failure, or even death.
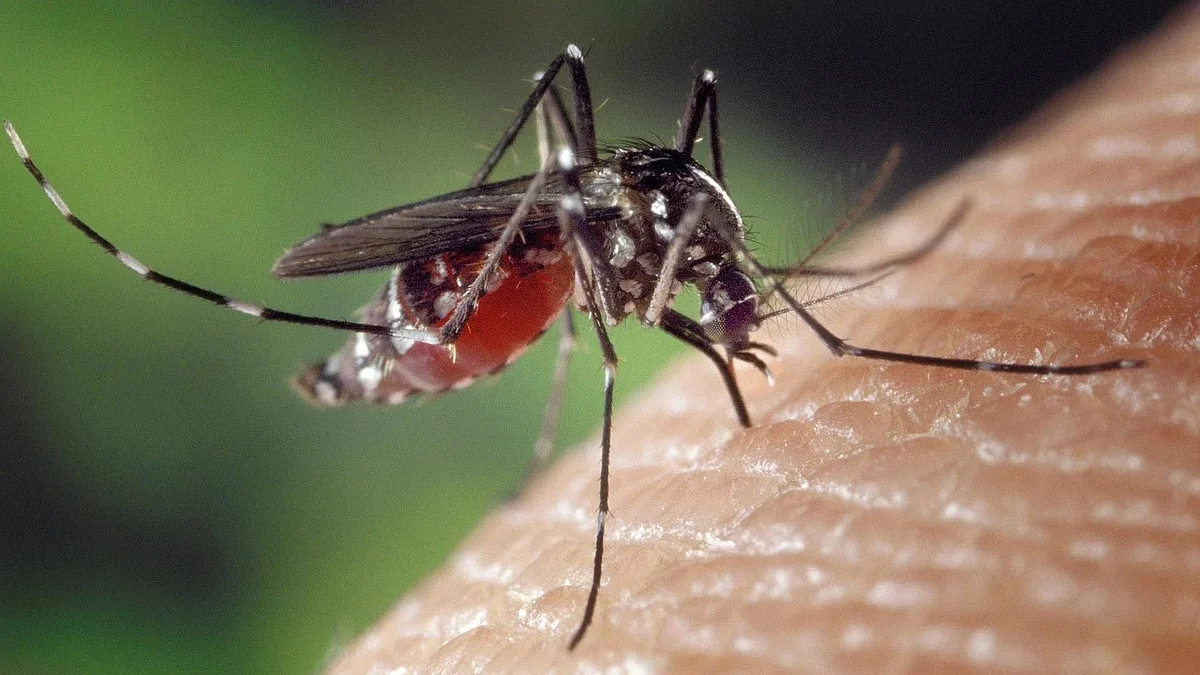
Causes of Malaria
Malaria occurs when a mosquito carrying Plasmodium parasites bites a person and injects the parasite into their bloodstream. Once inside, the parasites multiply rapidly, causing infection. Though mosquito bites remain the main mode of transmission, in rare instances, malaria can also spread through blood transfusions, organ transplants, or from mother to child during pregnancy.
Symptoms of Malaria
Malaria symptoms usually appear between one week and a month after infection, but in some cases, they may take longer. According to the medical reports, common signs include:
High fever and excessive sweating
Severe chills and body shakes
Headache and muscle aches
Fatigue and weakness
Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
Breathing difficulties and chest pain
Seizures in severe cases

As the illness progresses, malaria can cause anaemia and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes). If you experience these symptoms after being in a malaria-prone area, it is crucial to seek immediate medical care.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult your doctor for any concerns or questions regarding your health or medical condition.











